Convert Pundit CSV files to ghk / lbv / sdd¶
Introduction¶
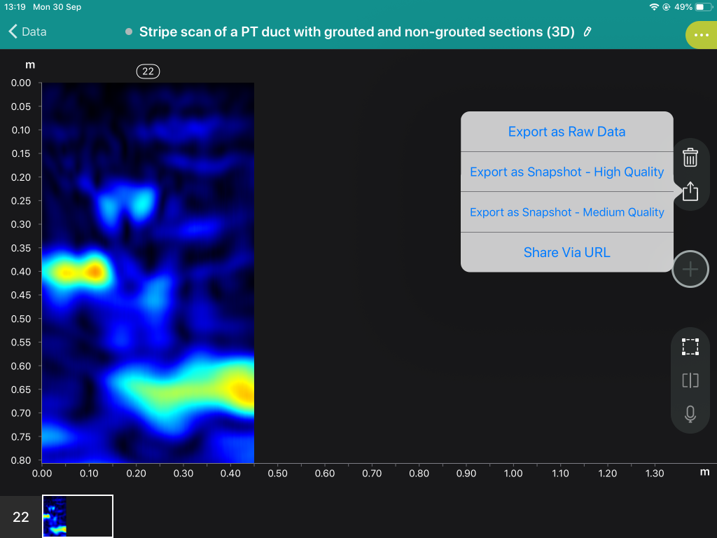
The Pundit Converter is a module in Pundit Vision software that analyse csv raw data files obtained with Proceq’s Pundit instruments and converts them into the binary data format required for the InterSAFT reconstruction module. The csv files can usually be opened from Microsoft Excel ™. However, the transfer algorithm from csv format to binary data format for InterSAFT is very sensitive, any modification applied to the csv raw data files may cause the files to be incorrectly converted. Below is a screenshot of the Pundit App on iPad showing the menu for exporting the csv Raw Data file.
Conversion Procedure¶
Important:
Before exporting the csv Raw Data file, the iPad language setting should be set to English.
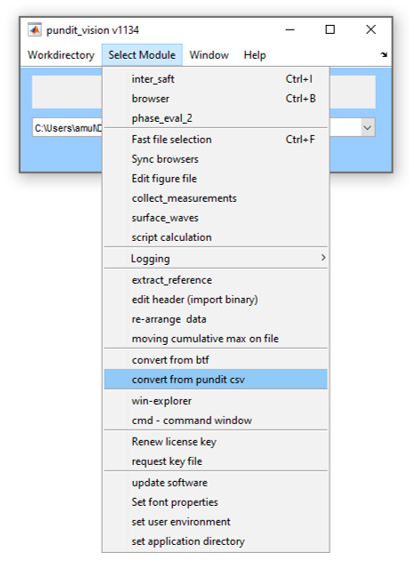
Once the raw data files are exported from the Pundit and imported into the PC, Pundit Vision can be started. Prior to using any module, setting the work directory to the folder containing the files to be converted is recommended, to do so click on Workdirectory in Pundit Vision’s main window. Then,click on Select Module then convert from pundit csv in the drop-down menu.
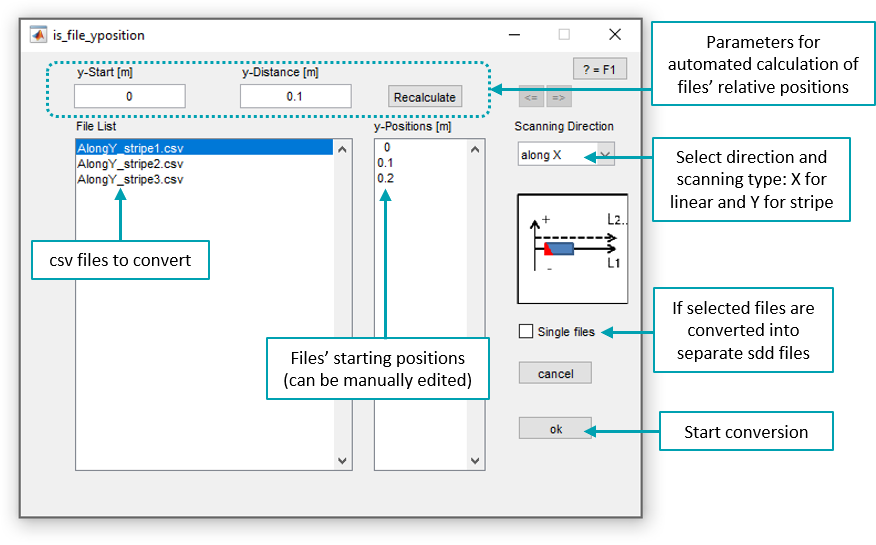
Select all the files to be converted. The conversion program can convert individual files or a whole serie of files. If several files are selected, they can be combined together into one file during the convertion process in which case their relative position should be specified from the menu. Alternatively checking the single files box means the files are converted separatly.
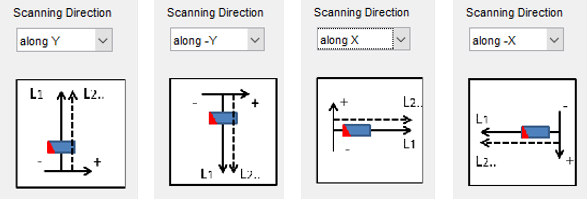
The scanning direction must be specified as it indicates the Pundit’s direction of displacement and the measurement mode (either linear or stripe scan). It is recommended to set the same measurement mode in the software as the one set in the Pundit’s iPad application during the data acquisition. The menu allows selecting between the following scanning directions:
“along Y” corresponds to stripe scans with the Pundit unit moved from left to right between each scan
“along -Y” corresponds to stripe scans with the Pundit unit moved from right to left between each scan
“along X” correspond to linear scans with the Pundit unit moved from bottom to top between each scan
“along -X” correspond to linear scans with the Pundit unit moved from top to bottom between each scan
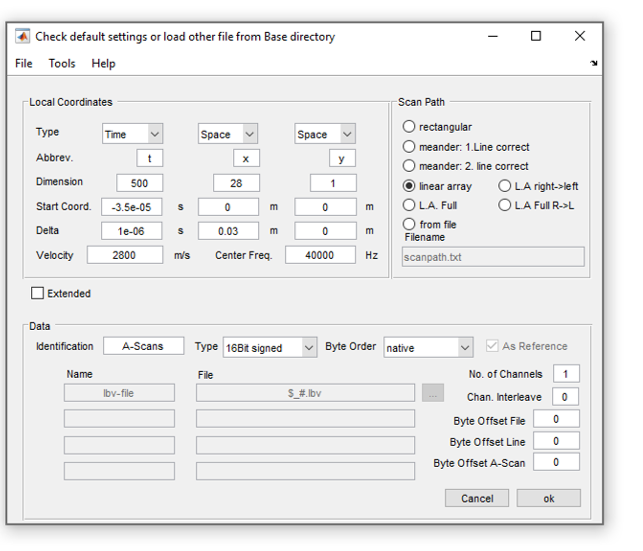
The conversion process extract and interpret the settings information and A-scans. The settings are stored in the header section(referred to as rf) of the output converted binary file. The interpreted header information is displayed on the screen after the conversion through a pop up window (as in example below), allowing to verify and eventually amend the information before saving the converted file.
Depending on the conversion set up (e.i., single or multiple files conversion), the convertion process produces files in ghk format or a combined sdd file with lbv files. In addition, for each converted file a ghk image is file created (for example: name_images.ghk). This image file contains contains the same reconstructed image as the one displayed in the Pundit application on the iPad, it can be used for comparison.
The Converted Data Format¶
In InterSAFT module we distinguish between measurement data of individual measurement positions or measurement series and position descriptions. The measurement data are stored in ghk files in binary form with binary header. If required, there is also a position description file (sdd format) in which more precise position information and further information about the relationship between individual ghk files are stored. (Sdd files are stored in Matlab format and could be opened with Matlab or other Matlab clones, if required).
Depending on the application, a ghk file is generated (simple measurement) or an lbv file with a sdd file. In InterSAFT module you have to open the ghk file or, if available, the sdd file.
Lbv files can only be opened together with a header file in InterSAFT. When you open an lbv file, you will be asked for a suitable header. In InterSAFT, a ‘default ghk header’ can be automatically adapted to the lbv file if certain boundary conditions are met. The header can then be further adjusted manually and saved for the lbv file so that the ghk file already exists the next time the lbv file is used and can be used directly.
When converting a csv file, a “default-ghk-header” is also required, which can be selected from a list for the proceq data. Some information is taken from the csv file and corrects the entries in the “default-ghk-header”. A query is made automatically in the converter. The selected header can then optionally be enriched with additional information. The header is saved in the sdd file and transferred to InterSAFT there.
Conversion of Pundit 250 Array (8-channel)¶
The conversion program can convert single files or a whole series of files. If several files are selected, the measuring positions can be moved to each other. The relative position can be set manually or equidistantly in the menu. The csv measurement file contains header information and the measurement data in the form of a table. Each csv file is converted into a binary data file with the extension .lbv. Since each measurement position of the device already provides a defined number of A-scans (depending on the length of the array), these signals always remain contiguous. For each of these measurement positions there is an entry in a sdd file that describes the exact position on the measurement field and the start address in the binary lbv file. Further device-specific information, some of which lies in the header area of the csv file, is taken from a ghk header file located in the user_settings directory for various devices and file formats. The user has to select the file (default header) and can add additional geometry and medium information. This header file also describes the format of the lbv file and is saved in the sdd file.
Execution of the conversion¶
start the converter from Pundit Vision
selection of the file or the file series
selection of scan direction, selection of start position and offset between measurement files
start the conversion
select the header file and customize (if necessary). The size of the measurement field, the array type and the scanning parameters are taken from the header of the csv file.
the conversion will be done and for each csv-file an lbv-file will be created
a sdd-file is created containing position information for all lbv-files
Execution of a reconstruction:¶
start the InterSAFT module
selecting a profile for Pundit files or a previous project
load the sdd file via “File -> Load Series Data Description (sdd)”.
initialize InterSAFT for the given measuring field with “Init-> Initialize Parameters”.
start the interactive reconstruction mode by “Start -> Start homogeneous SAFT”.
optimization of the settings
Check the conversion settings by displaying the Series Description parameters: “Linear Array -> Series description”. If parameters are changed here, the result must be saved in the sdd file or in a new sdd file and reloaded in InterSAFT if necessary, since a new initialization may be necessary due to the change of the position parameters.
start 2D- and 3D-reconstructions by “Start -> Prepare 3D-SAFT” etc. according to description
Hint:
The y and x positions that can be set in the menu refer only to the entire file. If a csv contains the data of several measuring lines, the distance between the measuring lines is not known for the converter. Therefore a manual input is queried. This information can be entered in two ways:
start coordinate in y-direction and constant offset of all measuring lines in y-direction (delta-y)
start coordinate in y-direction and vector of the relative y-coordinates. The input takes place in Matlab convention, i.e. “Start:increment:end” or “Position1, Position2, … PositionN”, where the number of positions must be at least as large as the number of measurement lines within the file.
If several measuring lines are in one file, a separate lbv file is created for each measuring line. A log file is created which shows the relationship between the csv files and the converted lbv files and the positions of the measuring points.
Used parameters of the csv file:¶
- The names of the parameters are derived from the names in the csv file:
‘software_version’,’scan_position_x’, ‘scan_position_y’, ‘panorama_offset’, ‘meas_type’, ‘overlap_of_bscans’,’ channels’,’ no_of_meas’,’ velocity’
Conversion of Pundit Live Array (8 to 16 Channel Linear Array)¶
Using the converter is simple: if a file exists, it will be converted into an lbv and a sdd file. If the coordinates in the file are selected correctly (x-axis is the long axis of the array), the positions (in rows or columns or in a 2D measurement field) are collected and entered into the sdd file together with the address of the respective data field in the lbv file. This sdd file is opened in InterSAFT and can be processed directly.
In case the positions are intentionally or accidentally arranged differently, one can swap the coordinate axes and change the scan direction.
Please note that the position of the array always runs in X direction, this is mandatory in InterSAFT. The scan direction, i.e. the coordinates specified in the csv file, can be interpreted differently. The changed scan direction is appended to the name of the created files so that different variants can be tested. Also the lbv files differ in the different cases, since the data in the lbv file are arranged according to the x,y coordinate system of InterSAFT. This means that the lower left measuring point is stored at the beginning of the lbv file.
The log file contains the assignment of the last conversion.
Special feature¶
The original format of the lbv file has been changed for this purpose: More than just the data of an array position can now be stored in an lbv file. However, in InterSAFT only the name of the lbv file belonging to a position is displayed in the table, but not the position in the file. If you select individual array positions, however, the log of the reading process shows the actual position in the black log window.
For graphical output it may be useful to display the lbv data in the Browser. For this you can use the “Linear Array - Series Definition” menu to merge the data of a column or all data into one ghk file. The position data in the resulting file can only be used to a limited extent, since ghk files contain only the positions of equidistant measuring points.
Merging several measurements into csv files¶
Prerequisite: All files have the same number of measuring positions per row (or column).
Procedure: When selecting the measurement files, select the files to be merged. Make sure that the file names can be sorted in the correct order. Manual sorting is not possible afterwards. This means that the file names must be numbered consecutively. The name of the sdd-file is determined suitably from the csv-filenames.
The process of conversion and reconstruction then takes place as described in section Execution of the conversion